



The Halal certification system is vital for customers who want to consume halal foodstuffs. In practice, different comments are made about halal products. However, many organizations are still making Halal certification. In halal certification studies, the source of the product or service is seen as very important for both businesses and consumers.

Consuming halal products produced with halal methods is an important necessity for Muslims wherever they live. According to Islamic principles, it is within the responsibility of Muslims to follow the norms and values of the holy books and hadiths in the best possible way in their daily lives.
Today Muslims live in different countries, such as India, Australia, Bangladesh, China, European countries, the United States and Canada, which do not practice Islam as an official religion. Therefore, the Muslim population constitutes an important market segment. Nevertheless, the food sector has somehow ignored the Muslim consumer segment until recently. Recently, however, the global Halal product sector has been developing very rapidly.
Especially Malaysia, Indonesia and some Asian countries are taking initiatives such as developing Halal standards, establishing traceability systems and establishing Halal science centers. In parallel, the European food sector is investing in the development of halal products. Some European retailers have added fresh halal meat to their range of food products. Some European companies even export halal products to Muslim countries. The Netherlands is a country with facilities that promote the development of a worldwide halal supply chain and store halal products for the first time.
Due to the facts described above, it is inevitable that demand for halal products and services, especially food products, will increase in the near future. The concept of halal is not just about food or food products. At the same time, a Muslim man goes beyond food to cover all aspects of his life.
The concept of halal is based on the need for any Muslim to consume religiously acceptable and permitted products. In this case, the concept of halal extends from food and beverages to banking and finance, tourism, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, business, travel, technology and transportation. Briefly, the concept of Halal is based on the principle that a product meets its Islamic requirements at its source. The two most important sources of Islamic rules are the Qur'an and the hadiths.
The fact that the companies operating in the food sector have obtained Halal Certificate provides many advantages for them. One of these advantages is to create trust. Consumers have the opportunity to make an informed choice when choosing foodstuffs.
With the halal food approach being accepted by non-Muslim people in terms of safety, hygiene and quality assurance, the halal food market is developing rapidly and in this respect, it is important for companies to have Halal Certificate to prove themselves in this direction. In this way, companies both increase their market opportunities and provide superiority to their competitors. Halal food sector has gradually increased its importance in the global market.
Companies with Halal Certificate are always prepared for legal audits and fulfill their obligations arising from legal regulations in a timely manner.
With the help of Halal certification, companies have proven their compliance with food safety, cleanliness and hygiene conditions while producing in accordance with religious conditions.
In Turkey, the following standards for Halal certification have been published by the Turkish Standards Institute (TSE) in 2011:
TS OIC / SMIIC 1 Halal food general guide
TS OIC / SMIIC 2 / T1 Guide for organizations with halal certification
TS OIC / SMIIC 3 Guide for accrediting body accrediting Halal certification bodies
TS OIC / SMIIC 4 Halal Cosmetics - General Rules
These standards are based on standards designed by the Institute of Standards and Metrology of Islamic Countries (SMIIC), based in Istanbul.
Today, Malaysia is the first country in the world to start issuing Halal Certificates. Halal food studies in this country are carried out by the Islamic Development Department (JAKIM) of the Government of Malaysia. World-wide halal food standards, accredited by the United Nations, have been prepared by the World Halal Foundation, based in Malaysia. This foundation has as many members as 60.
The Bible contains provisions on what kind of food Muslims should or should not consume. These provisions are relevant in all respects to human health. For example, dead animals are banned because they are harmful to human health due to decay. Similarly, blood flowing from an animal contains a number of hormones, bacteria and toxins that are harmful to human metabolism and body development. Therefore, according to Halal certification criteria, the following substances are considered haram for human consumption: animals not counted according to Islamic rules, animals slaughtered on behalf of someone other than Allah, domestic donkeys and mules, pork and by-products, alcohol and intoxicating substances, toxic plants, carnivorous animals with teeth such as lions, dogs, wolves and tigers, birds of prey such as eagles, falcons and owls, pests such as snakes, rats and scorpions, insects, blood and blood by-products, and contaminated foodstuffs.
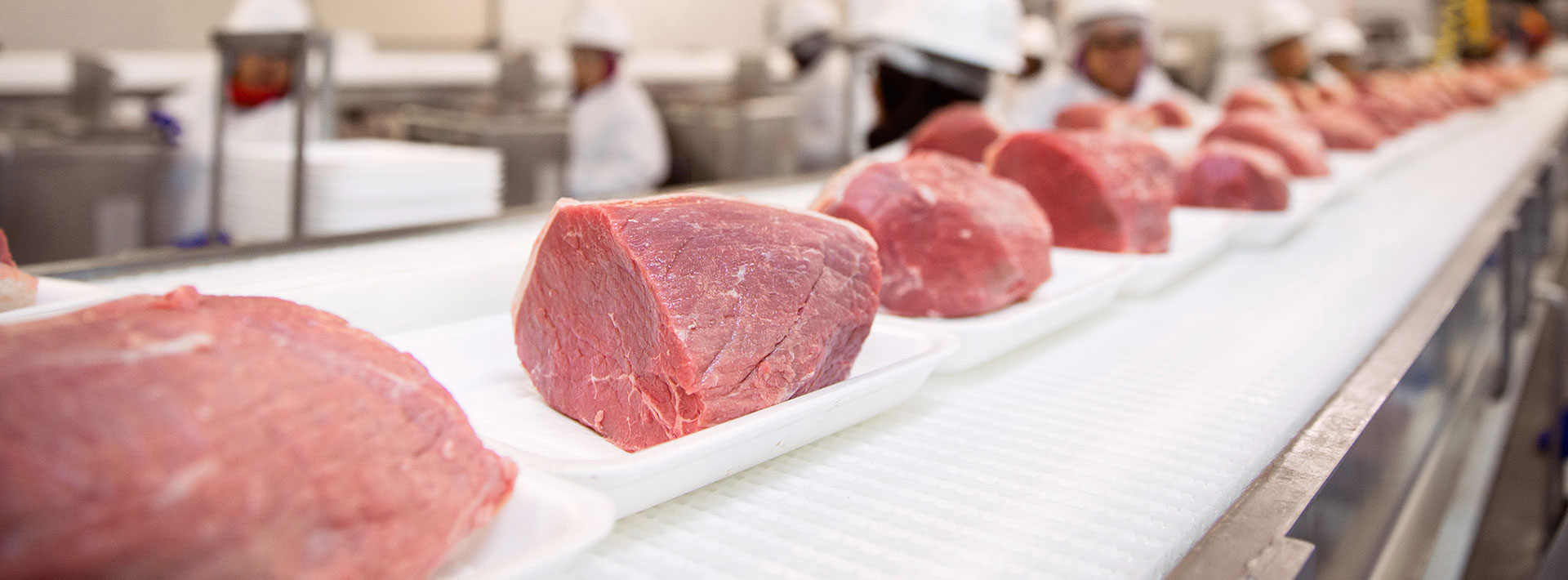
Meat is the most strictly regulated foodstuff in the Islamic religion, and consumers' awareness of the search for halal meat is particularly high among Muslim consumers in Asian, Middle Eastern and European countries. The prerequisite for meat to be halal is that it must come from animals such as cattle, sheep and goats. These animals should be raised naturally and alive during slaughter. Cutting operations should be done according to Islamic principles. The blood of the animal should be completely drained. Furthermore, the animal should not be injured or diseased before slaughtering. Even if all these criteria are met, according to the Halal concept, the meat must be protected against any contamination and remain halal until it reaches the consumer.
First, it is determined whether the organization meets the mandatory requirements of the standard and whether to proceed to the next stage.
It is checked whether necessary procedures and audits have been developed and your institution's readiness for evaluation is reviewed.
The findings that arise in the first two stages are evaluated and after all corrective actions are reviewed, document preparation is started.
To get an appointment, to get more detailed information or to request an evaluation, you can ask us to fill in our form and reach you.